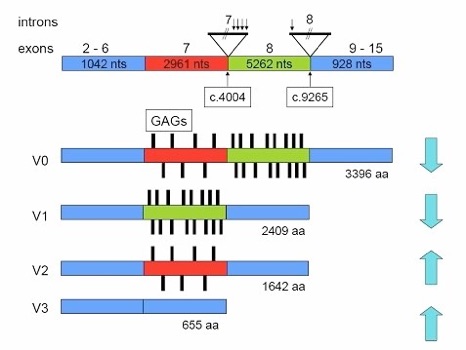
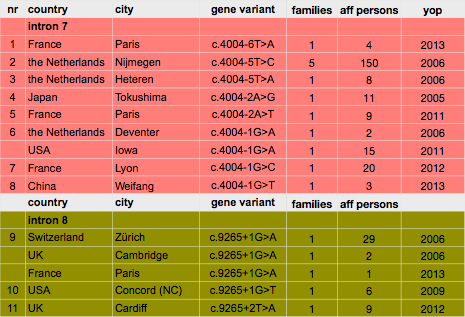
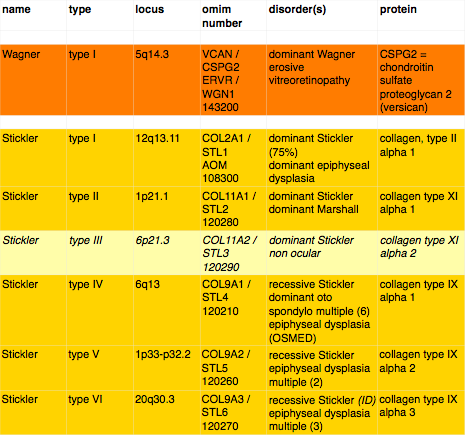
glossary
(ncbi-gene reviews)
isoforms
The protein products of different versions of messenger RNA created from the same gene by employing different promoters, which causes transcription to skip certain exons. Since the promoters are tissue-specific, different tissues express different protein products of the same gene.
RNA
synonym:
ribonucleic acid
The molecule synthesised from the DNA template; contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose, which is present in DNA; three types of RNA exist, messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
DNA
synonym: deoxyribonucleic acid
The molecule which encodes the genes responsible for the structure and function of an organism and allows for transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next
gene
The basic unit of heredity, consisting of a segment of DNA arranged in a linear manner along a chromosome. A gene codes for a specific protein or segment of protein leading to a particular characteristic or function.
transcription
he process of synthesising messenger RNA (mRNA) from DNA
splicing
synonym:
splicing mutation
The process by which introns, non-coding regions, are excised out of the primary messenger RNA transcript and exons (i.e. coding regions) are joined together to generate mature messenger RNA
exon
Coding sequence of DNA present in mature messenger RNA
nucleotide
A molecule consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, thymine, or cytosine in DNA; adenine, guanine, uracil, or cytosine in RNA), a phosphate group, and a sugar (deoxyribose in DNA; ribose in RNA). DNA and RNA are polymers of many nucleotides.